DRC: Violence by armed groups has exacerbated the nutritional situation in Masisi territory
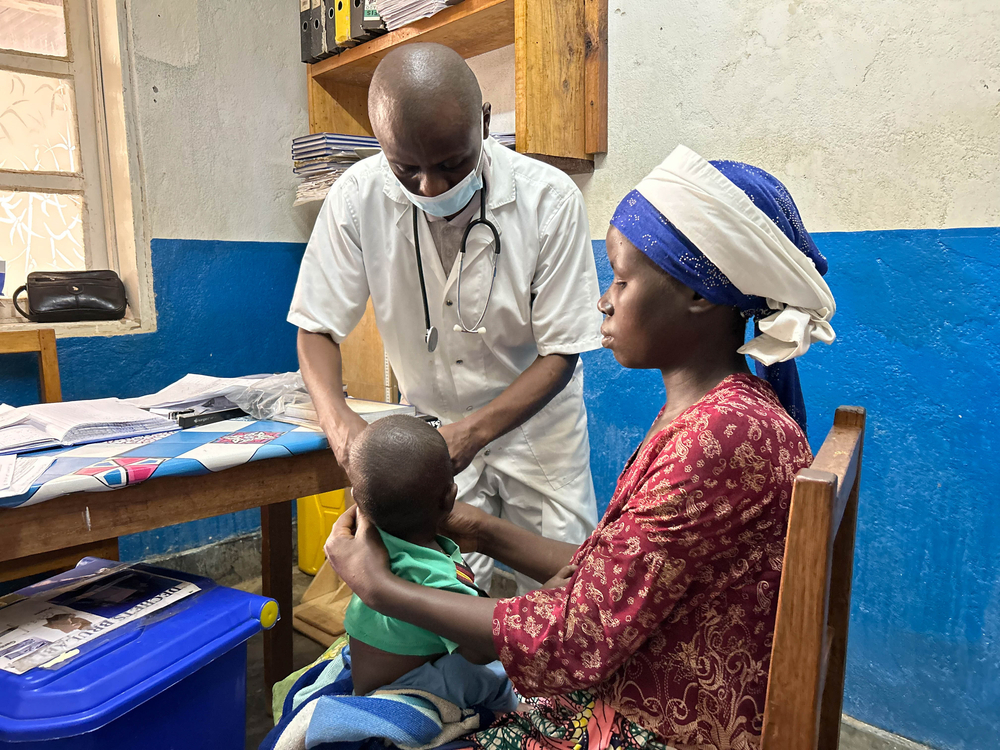
Since the beginning of the year, an average of 800 children suffering from severe acute malnutrition have been admitted each month for treatment to hospitals in Mweso and Masisi, almost double that of the previous year. This alarming situation is paradoxical given that Masisi territory, around 20 km northwest of the provincial capital, Goma, is renowned for its fertile green hills. The scene of armed conflict for years, Masisi territory has recently seen a resumption of armed clashes between the M23 movement, Congolese armed forces and various other armed groups, leading to many more people being displaced from their homes and worsening an already critical humanitarian situation.
Even though malnutrition is not a new challenge for the Masisi territory, medical teams have observed this year a worrying increase in the number of cases of severe acute malnutrition with complications. Between January and September 2023, nearly 7,500 children were treated in the Masisi and Mweso hospitals, where MSF teams have been supporting those of the Ministry of Health for over fifteen years.
“My child fell seriously ill, but what struck me most were his eyes: they were sunken and empty,” says Micheline, a displaced woman whose son was hospitalised in Mweso. “I rushed to the health centre and they transferred him to hospital. It’s the first time one of my children has suffered from malnutrition.”
The nutritional situation of children, including displaced families, has deteriorated abruptly this year, largely due to the upsurge in violence, which has a direct impact on the socio-economic situation of the population. There are few functional medical facilities and those that are open are often short of essential medical supplies. The health authorities struggle to support local medical facilities and supply them regularly with medications and with nutritional inputs such as the peanut-based therapeutic food used to prevent and treat malnutrition.
“My daughter started to swell gradually – first her face and then all over her body,” says Mandela, whose daughter is being treated in Masisi hospital, supported by MSF. “I took her to the health centre where they gave her some peanut-based paste, but not enough to allow her to recover. On the fourth visit, as her condition had worsened, the doctors referred her to Masisi hospital.”
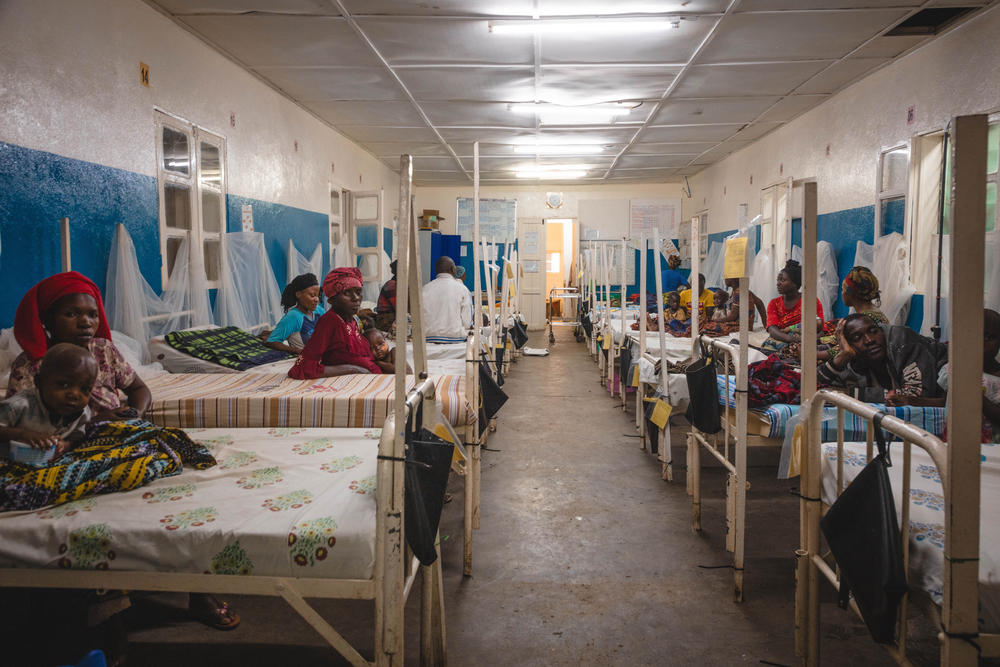

When children with moderate malnutrition fail to receive proper treatment in health centres, they are more likely to become severely malnourished and suffer medical complications, which are much more difficult to cure.
“If simple cases of malnutrition are not treated in the health centres, the number of hospital admissions increases,” says Dr Nadine Neema Mitutso, medical activities manager at Masisi Hospital. “Today, there are almost as many admissions to hospital intensive care units as there are to outpatient malnutrition programmes in health centres. Yet most of these hospital admissions could be avoided if children were treated in a preventive manner in health centres.”
After a child leaves hospital, families are faced with the same difficulties getting hold of both regular and therapeutic food, so the risk of relapse is high. “To put an end to this vicious circle, a holistic response needs to be provided by all actors in the region,” says Carole Zen Ruffinen, MSF project coordinator in Mweso.
“Sustainable solutions need to be found to meet the growing nutritional needs of the population.”
Violence disrupts normal life
Over recent months, the M23 group has moved into Masisi territory, where it has met with force by many local non-state armed groups, as well as Congolese armed forces.
These clashes have led to mass displacements of the population and hampered people’s access to fields, markets, schools, and medical facilities, exposing them to permanent food insecurity.
Masisi territory is characterised by its fertile hills, where agriculture remains the main economic activity and its communities depend on it to feed themselves. In recent months, access to the land has been more restricted by armed men setting up checkpoints and ‘tax points’ on the roads. People have difficulties reaching their land and are often forced to abandon them, leaving their crops unharvested.
“Because of the armed men, I can’t get to the fields every day,” says Fahida, whose son is in Masisi hospital. “When we take the road, we are afraid of meeting armed men along the way. They demand money and may even kill or rape us.”
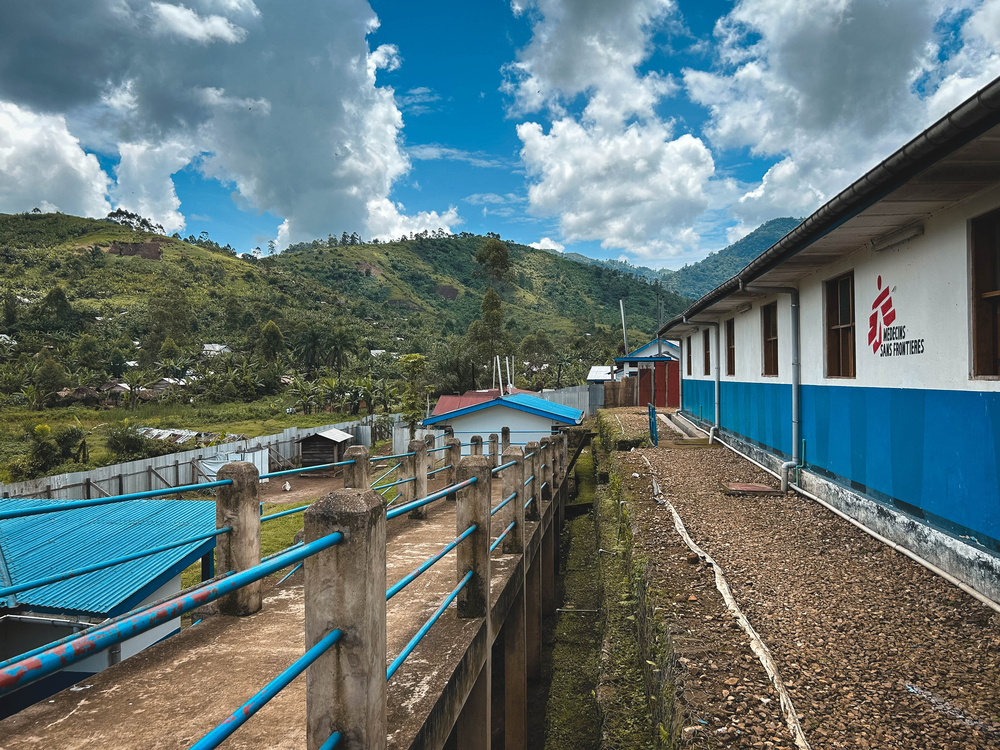

With people’s access to markets hampered, there has been a reduction in trade, while food shortages have led to a significant rise in prices. Last year, a bag of cassava flour cost around 500 Congolese francs ($0.28 CAD); since then it has quadrupled in price and now costs the equivalent of a day’s work in the fields, even though it is not enough to feed a family for a day.
“Back home, we never went a day without eating,” says Sifa, who took refuge with her family at the Katale site for displaced people four months ago after fleeing fighting in her home village. “But here we have nothing, our lives are miserable. Two months ago, my daughter Annika died of malnutrition in hospital. She was seven years old. We arrived [at hospital] too late. I tell you, poverty is going to kill us all.”
MSF calls on other organizations working in North Kivu to ensure a sustainable operational presence to prevent the disastrous consequences of malnutrition, and on Congolese authorities and donors to strengthen the medical response capacity of health facilities, particularly in terms of malnutrition treatment.
For 15 years, MSF has been providing free medical care in Masisi territory, supporting two general hospitals and twelve health centres in collaboration with the Ministry of Health. MSF teams also treat malnourished children in three inpatient therapeutic feeding centres, including one in the health centre of Nyabiondo in the Masisi health zone, as well as nine outpatient centres in Masisi and Mweso health zones. MSF also provides supplies of therapeutic food and essential medicines to treat malnutrition, while its health promotion teams raise awareness among local communities about the signs of malnutrition and the importance of getting timely treatment.